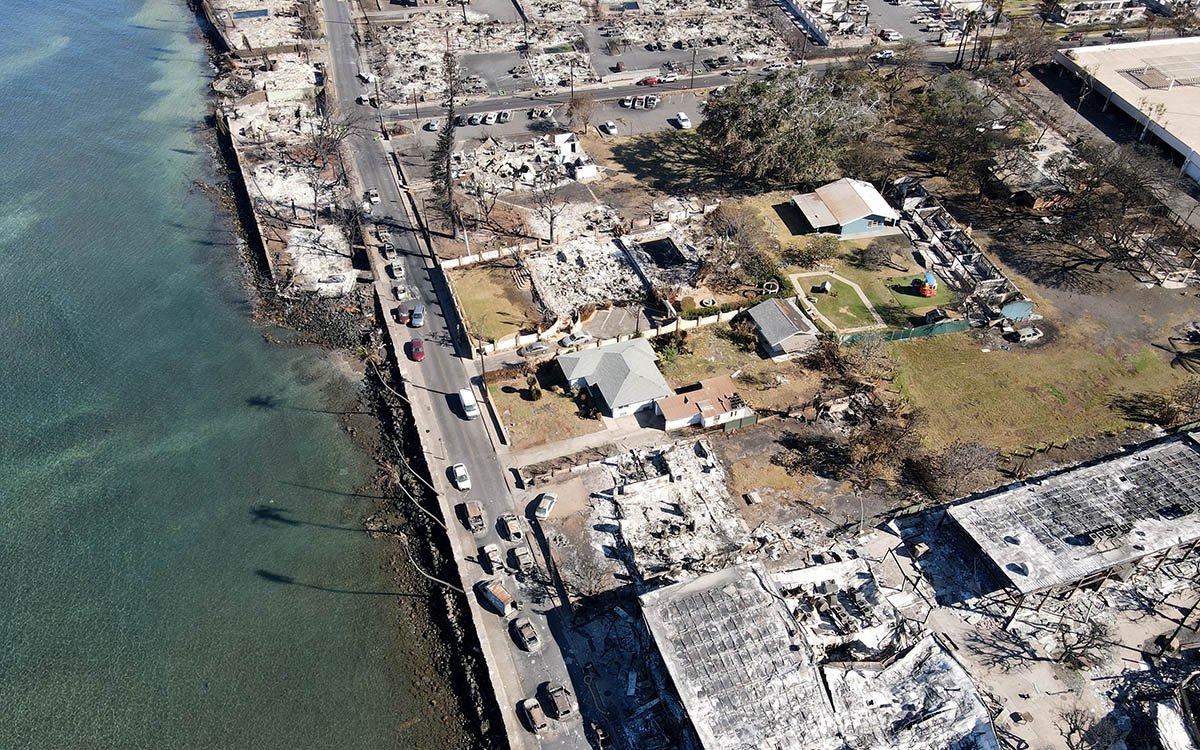
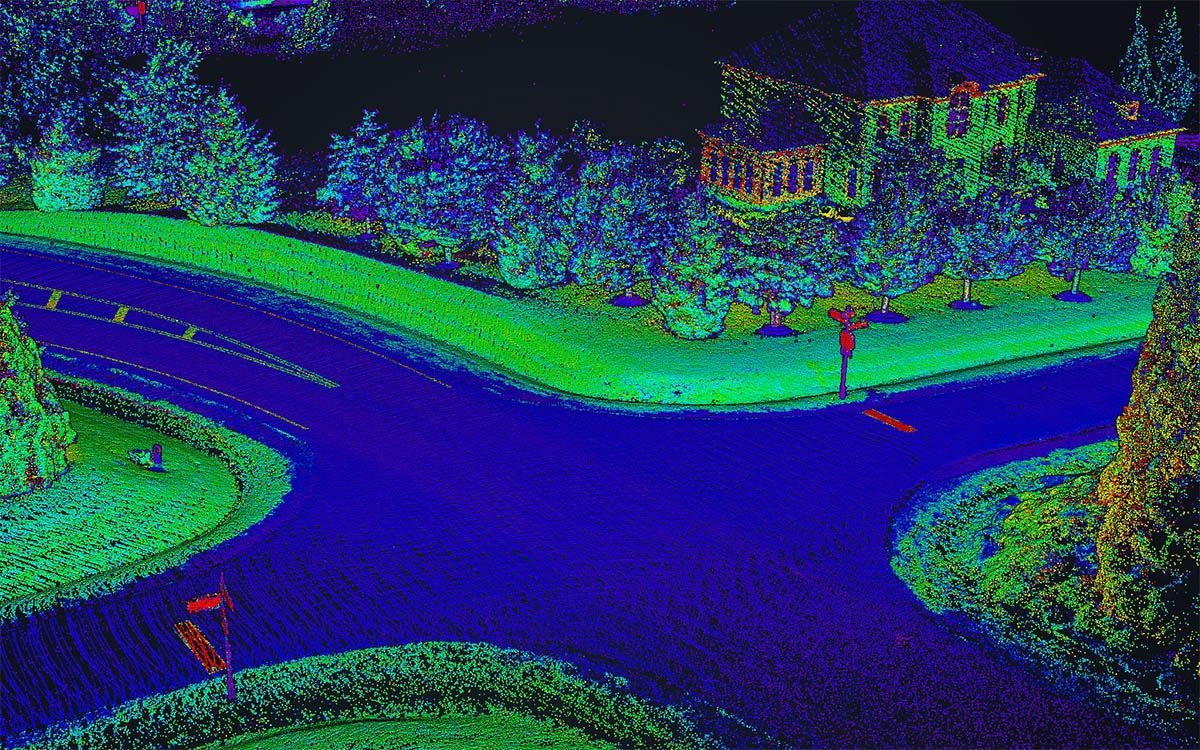
Ensuring our infrastructure is running and that our jobs and construction sites are safe should be a top priority. However, the maintenance and inspections needed are inherently dangerous and often time-consuming and repetitive, making drones instrumental and valuable tools.
Drones can capture all kinds of data from images and videos, LiDAR scanning, mapping data, and various data types related to air conditions, location, and precision location, including inertial data. As a result of using drones for these initial inspections, we can more quickly pinpoint the location and cause of the problem and ensure that fewer humans are put in harm’s way.
Use Cases
The construction industry began adopting drone tech as early as 2013 to collect real-time environmental data, survey difficult-to-access terrain, and track construction data. Since then, thousands of projects have successfully implemented drones from every aspect of construction, starting with design and building and ending with maintenance and razing.
Preconstruction Design and Site Review
Architects and builders find imagery and drone data particularly relevant in preconstruction. Using this data, they can get detailed terrain and, in some cases, soil composition and environmental data to help determine construction materials and estimate building costs. Furthermore, the visuals and precise data points help them in many ways, whether generating renderings of views from each floor or angle or using a new process like Building Information Modeling (BIM). BIM allows architects to design buildings using a single set of computer models instead of individual drawings.

Construction Monitoring
In addition to the terrain and survey maps from the design phase, drone data can help workers create accurate plans for prepping the construction site, including ground preparation, determining and mapping out temporary structures and roads, and estimating time and labor. Similarly, drone imagery is valuable for monitoring job progress and safety, quality control reports, and regulatory compliance.
Operations and Maintenance
Drones are a low-cost alternative for accessing remote or semi-remote locations or sending a person for high-risk visual inspections or damage assessments. With different data types and sensor inputs, drones allow users access to precise data and high-definition video and imagery, including thermal and infrared images, available to experts in real-time.
Razing
The role of drones in the deconstruction phase at the end of a building’s life is still emerging. They offer a safe option for capturing exciting videos of the process, but they can also provide engineers with essential data to plan their methodology, which is inherently dangerous.
After all, drone footage and data can help engineers mitigate dangers by giving them a better understanding of the state of the building. Resulting insights might include settling, damage from earthquakes or significant storms, any undocumented modifications to building plans or materials, and more.
What’s Next
The value of drones in construction and inspection continues to grow, particularly in energy, transportation, telecommunications, and existing infrastructure, including bridges, pipelines, and roadways.
Industries must ensure their software integrations can accept and parse drone data using powerful algorithms. Fortunately, many sensor manufacturers, including Inertial Labs, work with engineers to develop solutions and workflows that ensure data maximization. We constantly look for new ways to innovate and integrate our sensors, like the INS-B, for new applications.
Regulations must keep up with technology, and although governing bodies are catching up, the necessary rules don’t necessarily apply to emerging tech.
Engineers must also be mindful that the data doesn’t tell the whole story, so they must prepare to analyze data and put it into context for architects and construction companies. Adopting new processes and protocols, like BIM, is more than merely using drones and getting better data. Instead, we must bring all the players on board and show them the value.
Although there are varying forecasts for drone growth in the coming decades, one thing is sure: we have not yet seen the limits of their potential for improving industry and safety. The most accurate estimate comes from Goldman Sachs, suggesting that in the next 5 years, the global construction industry will generate about $11.2 billion, with $1.3 billion in the U.S. alone. The bottom line is that we can expect drones to grow in value and use in construction and inspections.