Value Added AHRS
Since its first release, the Inertial Labs Attitude and Heading Reference System (AHRS) has continued to develop and improve its performance and integration abilities. The newest addition, the AHRS-II-P, is a compact, lightweight, and affordable solution both as a standalone reference unit and a solution where applications involving the integration of an external compass or GNSS receiver may be needed to improve an existing system. Although the AHRS-II-P comes standard with an embedded fluxgate magnetometer to determine accurate Heading, input is supported for an external magnetic compass to increase static and dynamic accuracy. The AHRS-II-P offers advantages over its competitors present on the market by recording and transmitting very accurate Heading, Pitch, and Roll, a very appealing choice for applications involving motion control such as UAVs, aircraft, ships, or robotic devices.

Aside from the ability to be easily integrated with existing systems, the AHRS-II-P makes field calibrations easier than ever before. After the ARHS-II-P is mounted onto its carrier base, a quick calibration procedure is performed, and the device is ready. Among the many ways to perform these calibration procedures, the Inertial Labs option for an ‘On-the-Fly’ calibration is the most noteworthy.
Now, the AHRS Supports Data Input from External GNSS Receivers
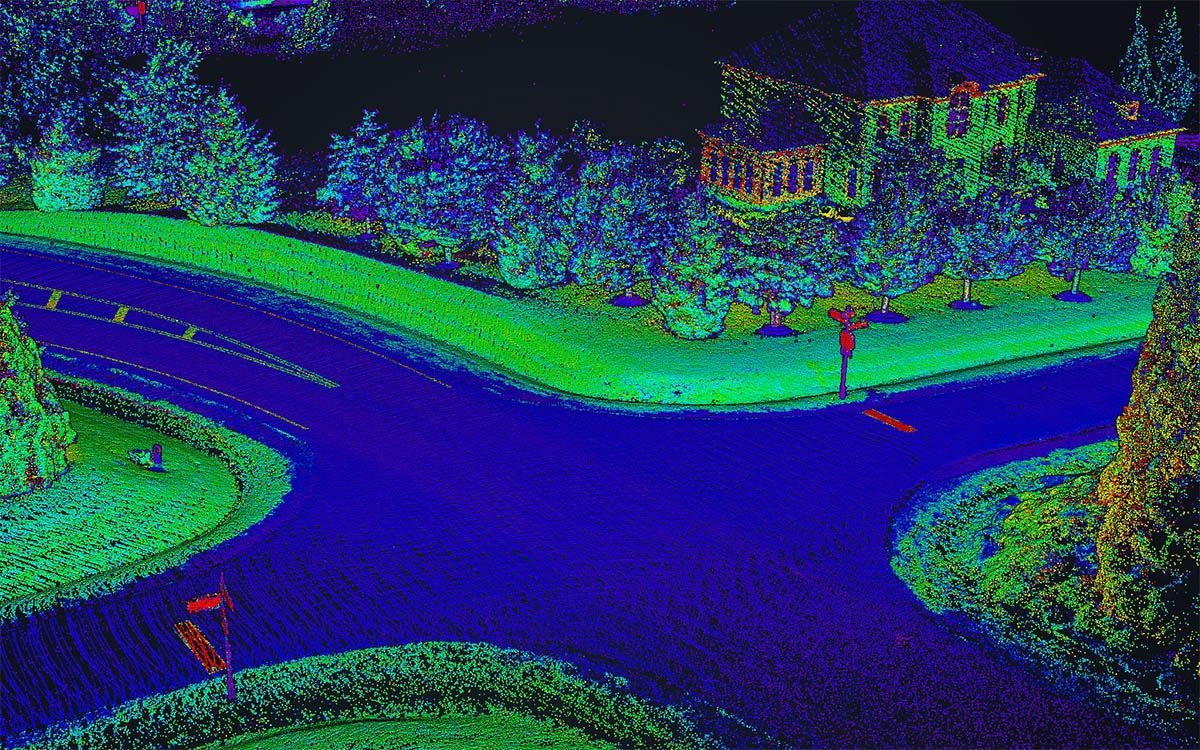
Inertial Labs is eager to present a recently implemented feature of the AHRS-II-P: the ability to utilize data from an external single or dual antenna Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver for position and velocity calculations and corrections. The AHRS-II-P expands its applicability and appeals to many potential use cases by adding this ability. Besides improving stable Heading course, it increases the accuracy of orientation calculations during maneuvers and positively affects dynamic accuracy overall. In addition, AHRS-II-P calculations and data outputs get synchronized with the respective clocks on the GNSS, which is, by default, much more accurate than internal system clocks. The standard unit utilizes powerful magnetometers to correct headings, but having GNSS data on top of that opens up the possibility of determining headings more accurately by over-ground tracking. The functional diagram on the right shows the flow of data for the AHRS-II-P utilizing an external receiver.
Functional Diagram of the Inertial Labs AHRS-II-P with External Inputs
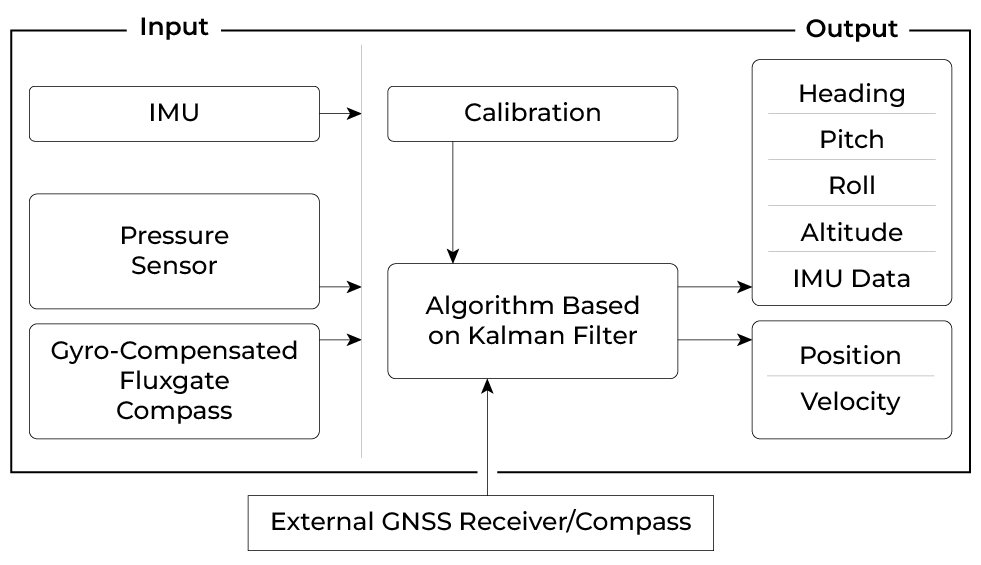
Here is A cost and functional comparison of the AHRS-II-P, AHRS-II-P with an external GNSS receiver, and a similar product from a competitor. We understand that every application has a particular set of requirements. Inertial Labs works hard to build a perfect solution for every application while ensuring the customer does not overpay. As you may see from the table, an external GNSS receiver alone would add several critical states of a system to the output. This would cover a wider variety of applications while, as you can see, still can stay at a competitive price when compared to one of its market’s competitors.
At Inertial Labs we aim to give customers an affordable, complete, and comprehensive solution by ensuring all customer requirements, including performance, come first, without cutting corners for quality.
Showcase Feature: On-the-Fly Calibration
The AHRS-II-P supports five hard and soft iron calibration types: 3D calibration, 2D-2T calibration, 2D calibration, VG3D calibration, and the new showcase method – ‘On-the-Fly’ VG3D calibration. This calibration method is designed for applications with limited pitch and roll angles. A common application need for this method lies with drone users. When ground calibration is too difficult to perform, the drone can take off and perform the calibration maneuver manually in flight to begin the calibration process, all the while real-time data acquisition functions like autopilot still work seamlessly. This ‘On-the-Fly’ method allows full calibration while a unit is in its normal operational mode without interrupting its orientation calculations or data outputs. Upon receiving a calibration start command, the AHRS-II-P starts gathering magnetometer data; at this time, the carrier object must perform a maneuver, rotating twice in full azimuth range with maximum possible pitch and roll ranges.

An example of this maneuver can be seen in the image above. In this figure, an airplane performs at least two full 360° coordinated turns, once towards each side (to the right and then to the left), with maximum roll angles. Once this maneuver has been made, the AHRS-II-P starts the VG3D calibration calculation. Newly calibrated parameters are applied to the AHRS-II-P magnetometer data flow stream, and the unit compensates immediately. During all steps of ‘On-the-Fly’ VG3D calibration, the AHRS-II-P unit continues operational calculations and the outputting of orientation data.
Test Results of the AHRS-II-P with External GNSS Input
For this test procedure, the Inertial Labs AHRS-II-P was mounted to the floor of a test vehicle. The external GNSS receiver was mounted to the ceiling, and the respective antenna was mounted on the roof of the vehicle. The test duration was approximately 25 minutes long, and was performed at an average speed of 25 mph (11.18 m/s) in the suburban area shown in the picture below.

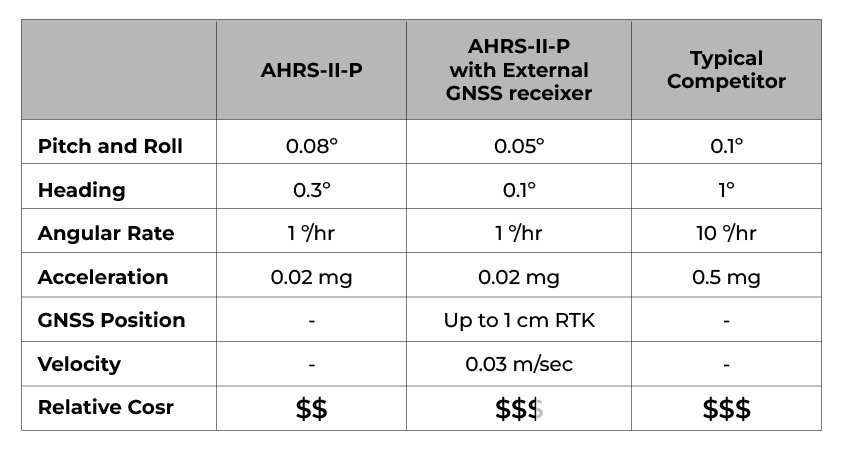
Values displayed below in the table are the errors determined by comparing the real-time results of the data acquired during the test and the post-processed data captured by a simultaneously run reference device. This reference device combines SPAN technology from NovAtel and a Ring Laser Gyro-based IMU, the HG1700, from Honeywell. Together, this ground reference provides immaculate RTK performance to use as a platform for analyzing sensor reliability.
Test Results of real-time readings from AHRS-II-P with and without an external GNSS receiver:
Recommendations on External GNSS Receivers
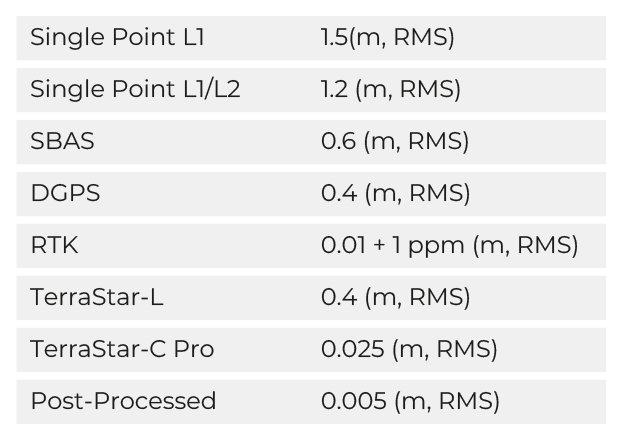
Connecting an external GNSS receiver to the AHRS-II-P requires a COM port with an RS-232/RS-422 interface. Use an external receiver with PPS output for timestamp synchronization for better performance. When choosing a GNSS receiver, it is crucial to be mindful of the available correction services. NovAtel offers different platforms, such as TerraStar, to get GNSS corrections. TerraStar correction services can provide outstanding position accuracy for almost any application using a global network of reference stations and advanced algorithms. Combining the services from TerraStar that NovAtel offers with the advanced Kalman filter algorithms inside products like the Inertial Labs AHRS-II-P, you can achieve post-processed position accuracy down to 0.005 meters.
Specifications of Position for Recommended NovAtel GNSS Receiver*
AHRS-II-P
The Inertial Labs AHRS-II-P is the next generation of enhanced, high-performance strap-down systems that determine absolute orientation (Heading, Pitch, and Roll) for any device it is mounted on. Orientation is determined with high accuracy for static or dynamic bases. The Inertial Labs AHRS-II-P utilizes Tactical-grade IMU (Gyro bias in-run stability of 1ᵒ/hr): 3-axes of precision accelerometers & gyroscopes each, and Ultra high-precision gyro-compensated Fluxgate Compass. Integration of gyroscopes’ output provides high-frequency, real-time measurement readings. IMU and Fluxgate magnetometer measure absolute pitch, roll, and magnetic Azimuth at initial alignment, and ongoing corrections are applied to gyroscopes during operation.